Ultimate Eye Care Guide: Tips to Protect Your Vision and Maintain Healthy Eyes Naturally
"Comprehensive Eye Care Tips: How to Protect Your Vision and Boost Eye Health at Any Age"
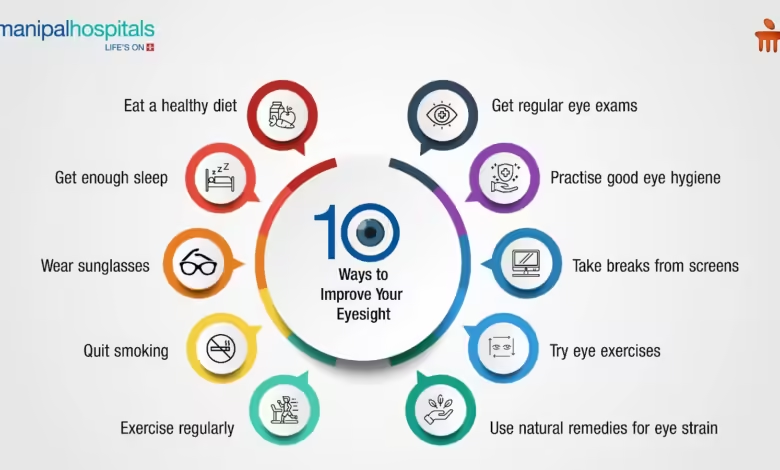
The Ultimate Guide to Taking Care of Your Eyes: Protecting Vision for a Lifetime
Your eyes are precious. They are your window to the world, allowing you to take in the beauty of nature, read the words of a book, and interact with loved ones. With modern lifestyles that often involve long hours in front of screens and exposure to environmental stressors, taking care of your eyes has never been more important. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into how to care for your eyes, discussing preventive strategies, lifestyle changes, and treatments that can help ensure your vision stays sharp for years to come.
1. Understanding the Importance of Eye Care
Your eyes play an essential role in your overall health. Many eye problems develop slowly over time and can be difficult to detect in the early stages, which is why regular eye care and check-ups are crucial. Taking proactive steps to care for your eyes can prevent common problems like dry eye, digital eye strain, and age-related vision loss.
Why Vision Health is Important
- Detecting Early Disease: Some eye diseases like glaucoma and macular degeneration may not have obvious symptoms in the early stages but can be detected through regular eye exams.
- Quality of Life: Good vision is essential for performing everyday tasks such as reading, driving, and using electronic devices.
- Preventing Eye Fatigue: Eye fatigue from digital devices is a growing problem. Proper care and prevention can help reduce strain and maintain productivity.
2. The Role of Diet in Eye Health
A balanced diet plays a vital role in maintaining eye health. Certain vitamins and nutrients have been shown to reduce the risk of eye diseases and promote good vision.
Essential Nutrients for Eye Health:
- Vitamin A: Helps protect the surface of the eye and is essential for good night vision. Foods rich in Vitamin A include carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens.
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Found in green leafy vegetables, these antioxidants help protect the eyes from harmful light and may reduce the risk of cataracts and age-related macular degeneration.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish like salmon and sardines, omega-3s reduce the risk of dry eye and protect the retina.
- Vitamin C and E: These vitamins protect the eye’s tissues from oxidative damage and may slow the progression of cataracts.
Foods That Support Eye Health:
- Carrots and Sweet Potatoes: Rich in beta-carotene, a precursor to Vitamin A.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach and kale are packed with lutein and zeaxanthin.
- Fish: Fatty fish such as salmon contain omega-3 fatty acids that help support the eyes’ structures.
- Citrus Fruits: Oranges and grapefruits are high in Vitamin C.
3. Protecting Your Eyes from Digital Devices
With the rise of digital technology, most of us spend hours in front of screens—whether for work, entertainment, or social interaction. This can lead to a condition known as digital eye strain or computer vision syndrome.
Signs of Digital Eye Strain:
- Eye Fatigue: A feeling of tiredness or discomfort in the eyes.
- Dry Eyes: Staring at screens reduces the frequency of blinking, leading to dryness.
- Blurred Vision: Difficulty focusing after prolonged screen use.
- Headaches: Eye strain can sometimes result in tension headaches.
Tips to Prevent Digital Eye Strain:
- Follow the 20-20-20 Rule: Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds to reduce eye strain.
- Adjust Your Screen Position: Keep your screen at eye level and about 20-30 inches from your eyes.
- Use Anti-Glare Screens: Reducing screen glare can minimize the strain on your eyes.
- Blue Light Glasses: These glasses filter out the blue light emitted by screens, which can contribute to digital eye strain and interfere with sleep.
4. Preventing Eye Injuries and Protecting Your Eyes
Eye injuries can happen in a variety of settings, from working with power tools to playing sports. Taking precautions can significantly reduce the risk of injury.
Common Eye Hazards:
- UV Radiation: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can increase the risk of cataracts and other eye diseases.
- Chemicals: Cleaning products, pesticides, and even cosmetics can irritate the eyes.
- Physical Trauma: Accidental blows or cuts to the eyes can cause serious damage.
How to Protect Your Eyes:
- Wear Sunglasses: Choose sunglasses that block 100% of UV rays to protect your eyes from the sun.
- Safety Goggles: When working with chemicals, power tools, or engaging in sports, always wear protective goggles.
- Be Mindful of Makeup: Be sure to remove eye makeup before going to bed to avoid irritation and eye infections.
5. The Importance of Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are essential for maintaining good eye health and catching problems early. Even if you don’t wear glasses or contacts, it’s still important to have your eyes checked regularly.
Types of Eye Exams:
- Comprehensive Eye Exam: This includes tests for vision sharpness, glaucoma screening, and checking for cataracts and macular degeneration.
- Retinal Imaging: Some eye care professionals use advanced imaging techniques to take a detailed picture of the retina to detect early signs of disease.
Frequency of Eye Exams:
- Children: Children should have their first eye exam at six months, another at age three, and just before starting school.
- Adults Under 40: An eye exam every two years is generally sufficient unless you have a pre-existing condition.
- Adults Over 40: After 40, more frequent exams are recommended, as the risk of eye diseases such as glaucoma, cataracts, and macular degeneration increases.
6. Managing Common Eye Conditions
There are many common eye conditions that can be managed with proper care and treatment.
Dry Eyes:
- Causes: Prolonged screen time, environmental factors, or underlying medical conditions.
- Treatment: Artificial tears, reducing screen time, or prescription eye drops.
Glaucoma:
- Causes: A buildup of pressure in the eye that can lead to optic nerve damage.
- Treatment: Eye drops, medications, or surgery to lower eye pressure.
Cataracts:
- Causes: Age-related clouding of the eye’s lens.
- Treatment: Cataract surgery is a common and effective procedure.
Macular Degeneration:
- Causes: Deterioration of the central part of the retina, leading to vision loss.
- Treatment: While there is no cure, lifestyle changes, medications, and certain vitamins can slow progression.
7. Eye Care for Different Age Groups
Your eye care needs change throughout your life. It’s important to understand how to care for your eyes at every stage of life.
Eye Care for Children:
- Develop Good Habits Early: Encourage children to take breaks from screens and spend time outdoors to prevent eye strain.
- Eye Safety: Ensure children wear protective eyewear when playing sports or engaging in activities that could harm their eyes.
Eye Care for Adults:
- Manage Screen Time: As adults often spend long hours working on computers, it’s essential to take regular breaks and follow good eye care practices.
- Monitor Health: Adults should keep track of any changes in vision and schedule regular eye exams to catch problems early.
Eye Care for Seniors:
- Cataract Prevention: Protect your eyes from UV exposure to reduce the risk of cataracts.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity promotes overall health, including eye health.
- Healthy Diet: Seniors should continue eating a nutrient-rich diet that supports eye health.
8. Natural Remedies for Eye Care
In addition to medical treatments, there are natural remedies that can help maintain eye health and reduce symptoms of common conditions like dry eye and irritation.
Warm Compress:
A warm compress can provide relief for dry eyes or styes by stimulating tear production and unclogging oil glands around the eyes.
Aloe Vera Gel:
Applying a small amount of aloe vera gel around the eyes can help soothe irritated or inflamed skin.
Cucumber Slices:
Placing cool cucumber slices on the eyes for 10-15 minutes can help reduce puffiness and hydrate the skin around the eyes.
9. The Role of Sleep in Eye Health
Getting enough sleep is crucial for your eyes to rest and recover. Sleep deprivation can lead to symptoms such as dry eyes, blurred vision, and eye strain.
Tips for Better Sleep:
- Establish a Routine: Going to bed at the same time each night promotes healthy sleep patterns.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: The blue light from screens can interfere with your sleep cycle, so try to avoid digital devices for at least an hour before bed.
- Create a Relaxing Environment: Make your bedroom a peaceful space with dim lighting and comfortable bedding.
10. Common Myths About Eye Care
There are many myths surrounding eye care, and it’s important to separate fact from fiction to properly care for your eyes.
Myth 1: Reading in Dim Light Will Damage Your Eyes
While reading in dim light can cause temporary eye strain, it does not cause permanent damage to your vision.
Myth 2: Eating Carrots Will Improve Your Vision
While carrots are rich in Vitamin A and are good for your eyes, eating them will not improve your vision beyond what is normal for you.
Myth 3: You Don’t Need an Eye Exam if Your Vision is Fine
Even if you aren’t experiencing vision problems, regular eye exams are crucial for detecting diseases like glaucoma that don’t have early symptoms.
Conclusion
Taking care of your eyes is essential for maintaining good vision and overall health. From regular eye exams and a healthy diet to protective measures and proper sleep, there are many ways you can support your eye health. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you can reduce your risk of developing common eye conditions and ensure that your vision remains sharp for years to come.
Your eyes deserve the best care—so make eye health a priority today!

